Proteins may be broken into their constitutent monomer molecules by hydrolysis. AminoAcid products of the reaction constitute the AminoAcid composition of the Proteins.
Standard AminoAcid : 20 amino acids found in Proteins
Nonstandard AminoAcid : chemically mdified after their incorporation into a polypeptide and amino acids that occur in living organisms but are not found in Proteins. e.g.taurin
These molecules contain a central carbon atom (alpha-carbon) to which an amino group, a carboxylate group, a hydrogen atom, and an R(side chain) group are attached.
At a pH of 7 the carboxyl group of an AminoAcid is in its conjugate base form (-COO-) and the amino group is in its conjugate acid form (-NH3+). Thus each AminoAcid can behave as either an acid or a base. It's called Amphoteric property of a AminoAcid. Neutral molecules that bear an equal number of positive and negative charges simultaneously are called zwitterions. It is the R group, however, that gives each AminoAcid its unique properities. Also the pH value that AminoAcid's net charge become zero is called IsoelectricPoint.
Names and Abbreviations of the Standard amino acids
AminoAcid |
Three-Letter |
One-Letter |
Alanine |
Ala |
A |
Arginine |
Arg |
R |
Asparagine |
Asn |
N |
Aspartic acid |
Asp |
D |
Cysteine |
Cys |
C |
Glutamic acid |
Glu |
E |
Glutamine |
Gln |
Q |
Histidine |
His |
H |
Isoleucine |
Ile |
I |
Leucine |
Leu |
L |
Lysine |
Lys |
K |
Methionine |
Met |
M |
Phenylalanine |
Phe |
F |
Proline |
Pro |
P |
Serine |
Ser |
S |
Threonine |
Thr |
T |
Tryptophan |
Trp |
W |
Tyrosine |
Tyr |
Y |
Valine |
Val |
V |
Special AminoAcid
Sec |
U |
Classification of Amino acids
- Group I : Hydrophobic - Nonpolar side Chains
- Ala, Val, Leu, Ile, Pro, Met, Phe, Trp
- Gly, Ser, Thr, Cys,Tyr, Asn, Gln
- Asp, Glu
- Lys, Arg, His
Properties of each Amino acids
♣Histidine(His, H)
- Unique imidazole side chain: effective as nucleophilic catalyst( more basic than hydroxide ion)
five-membered ring structure --> relatively little steric hindrance pKa = 7
<Aromatic Residues>
- Has UV absorbance and fluorescence properties of proteins.
AminoAcid chart
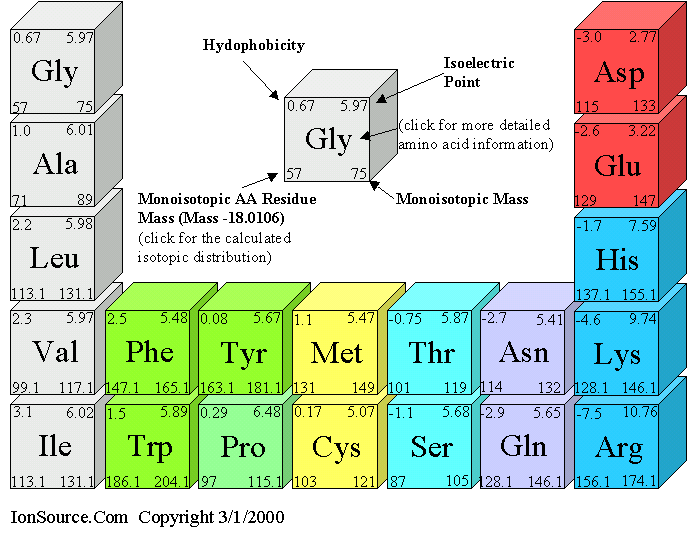
필수 AminoAcid
체내에서 합성이 되지 않기 때문에 반드시 섭취해야 하는 8가지 AminoAcid들
- Ile, Leu, Val, Lys, Phe, Trp, Met, Thr