|
Size: 745
Comment:
|
← Revision 6 as of 2011-08-03 11:00:49 ⇥
Size: 751
Comment: converted to 1.6 markup
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 8: | Line 8: |
| I(A;B) = H(A)-H(A|B) = \sum_{i=1}^r \sum_{j=1}^s P(a_i, b_j) \log_2 \frac{P(a_i, b_j)}{P(a_i)P(b_j)} | $$ I(A;B) = H(A)-H(A|B) = \sum_{i=1}^r \sum_{j=1}^s P(a_i, b_j) \log_2 \frac{P(a_i, b_j)}{P(a_i)P(b_j)} $$ |
| Line 10: | Line 10: |
[[BR]] |
<<BR>> |
| Line 14: | Line 12: |
| I(A;B) = H(B)-H(B|A) = H(A) + H(B) - H(A,B) | $$ I(A;B) = H(B)-H(B|A) = H(A) + H(B) - H(A,B) $$ |
상호정보량. InformationTheory에서 개별 정보량과 구분되는것.
MutualInformation is the communication rate in the presence of noise.
ai와 bi의 결합확률로 평균한 것을 입력알파벳 A와 출력알파벳 B의 MutualInformation이라고 부르고, I(A;B)라고 쓴다.
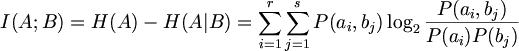
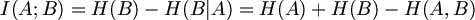
상호정보량의 의미는 B를 앎으로써, A를 표현하는 데 필요한 비트수가 몇 비트 절약될 수 있는가를 나타내고 있다. 일반적으로 A와 B에 공통으로 포함된 정보량이라고 표현할 수 있다.
 BioHackersNet
BioHackersNet